1. History and Founding
Apple Inc. was founded on April 1, 1976, by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak,
and Ronald Wayne in Cupertino, California, USA. The company started as
a personal computer manufacturer with the release of the Apple I and
later the Apple II, which became one of the first mass-produced
personal computers.
In 1984, Apple introduced the Macintosh, revolutionizing the computing
industry with a graphical user interface. However, internal conflicts
led to Steve Jobs leaving the company in 1985. Apple struggled in the
1990s but saw a massive turnaround when Jobs returned in 1997. He
introduced a series of groundbreaking products, including the iMac,
iPod, iPhone, and iPad, transforming Apple into a tech giant.
Today, Apple is one of the world’s most valuable companies, known for
its innovation, premium branding, and strong ecosystem of products and
services.
2. Sector and Industry
Apple operates in the broader technology sector and is a key player in
several multi-billion-dollar industries. At its core, Apple is a
consumer electronics company—but its reach extends far beyond devices.
It competes in software, cloud services, digital payments, streaming,
and health tech. This cross-industry presence is what makes Apple
unique.

Apple’s ecosystem spans devices, software, services, and media
platforms.
Its main areas of operation include:
-
Consumer Electronics: iPhone, Mac, iPad, Apple
Watch, and AirPods are among the world’s best-selling devices.
-
Software & Services: iOS, macOS, iCloud, and
Apple’s app ecosystem serve over 2 billion active devices.
-
Digital Media & Payments: Apple TV+, Apple Music,
and Apple Pay compete with Netflix, Spotify, and PayPal.

Apple's services segment includes Apple Music, TV+, iCloud, App
Store, and more.
Apple’s closest competitors include tech giants like Microsoft, Google
(Alphabet), Samsung, Amazon, and Meta. Its ability to operate across
industries gives it a strategic edge that few can match.
3. Revenue Streams – How Apple Makes Money
a) Hardware Sales (Major Contributor - ~80% of Revenue)
-
iPhone – The biggest revenue driver, accounting for ~50% of sales
- Mac & iPad – Premium computers and tablets
- Wearables & Accessories – AirPods, Apple Watch, HomePods
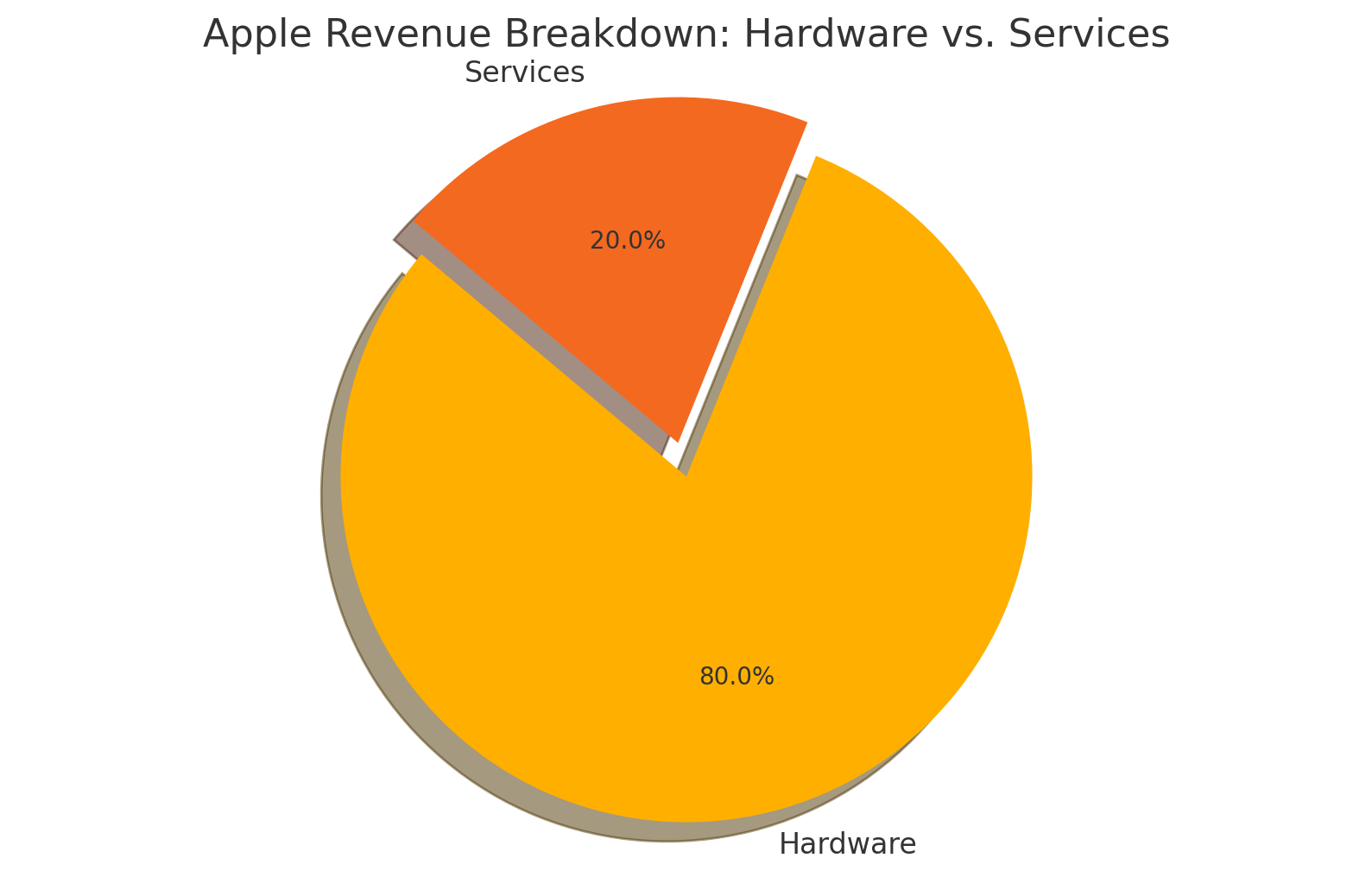
Apple’s revenue is driven mostly by hardware, with services gaining
ground.
b) Services (Fastest Growing - ~20% of Revenue)
- App Store & In-App Purchases – 30% commission on app sales
-
Subscription Services – Apple Music, iCloud, Apple TV+, Apple Arcade
- Apple Pay & Financial Services – Growing revenue stream
Apple’s subscription business is growing rapidly, providing recurring
revenue and reducing reliance on hardware sales.
4. Competitive Advantage & Strengths
-
Strong Brand Loyalty – One of the most recognized and trusted brands
globally.
-
Ecosystem Effect – Seamless integration between iPhones, Macs,
iPads, and services keeps customers locked in.
-
High Profit Margins – Apple has some of the best margins in the
industry due to premium pricing.
-
Continuous Innovation – Investment in R&D ensures Apple remains a
leader in tech.
-
Cash Reserves & Strong Financials – Apple has one of the largest
cash reserves among corporations, allowing flexibility in
investments, acquisitions, and shareholder returns.
5. Strategic Ecosystem & Partnerships
Apple’s strength lies not only in its products but also in its
extensive network of partners and a deeply integrated ecosystem. These
relationships enhance scalability, performance, and customer loyalty.
Key Partners:
-
Foxconn & TSMC: Critical manufacturing and chip
design partners.
-
App Developers: The App Store thrives thanks to
millions of independent developers.
-
Financial Institutions: Partners like Goldman Sachs
help power services like Apple Card and Apple Pay.
-
Content Providers: Partnerships for Apple TV+
original content and distribution.
Owned Ecosystem:
-
Operating Systems: iOS, macOS, watchOS, iPadOS –
all controlled by Apple.
-
Apple Silicon: Custom chips (M1, M2) designed for
high performance and efficiency.
-
Digital Services: iCloud, Apple Music, TV+, Arcade,
Fitness+.
This ecosystem strategy ensures Apple retains control over user
experience, reduces dependencies, and drives high-margin recurring
revenue through services.
6. Risks & Challenges for Investors
-
Dependence on iPhone Sales: The iPhone still
generates over half of Apple’s revenue. Any slowdown in global
smartphone demand or iPhone upgrades could impact financial
performance.
-
Regulatory Scrutiny: Apple faces increasing
antitrust investigations in the U.S., EU, and other
regions—particularly around App Store practices and competitive
fairness.
-
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Heavy reliance on
Chinese manufacturing exposes Apple to risks from geopolitical
tensions, pandemics, or labor disruptions.
-
Market Saturation: In developed countries, most
people already own smartphones and computers, making it harder for
Apple to grow hardware sales significantly.
-
Environmental & Ethical Pressure: Investors are
watching how Apple handles e-waste, carbon neutrality goals, and
sourcing materials ethically.
7. Future Growth Opportunities

The Apple Vision Pro represents Apple’s entry into spatial computing
and immersive technology.
-
Augmented & Virtual Reality (AR/VR): The Apple
Vision Pro headset is Apple’s bold first step into spatial
computing. This market could reshape how users consume media, work,
and communicate.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Apple is investing
heavily in on-device AI. With major updates coming to Siri and iOS,
the company aims to integrate AI deeply into its user experience
without compromising privacy.
-
Electric Vehicles (EVs): Though the “Apple Car”
project remains secretive, any entry into autonomous or electric
mobility could open a massive new revenue stream.
-
Healthcare & Wearables: The Apple Watch and Health
app are evolving into powerful tools for preventive care,
diagnostics, and health tracking, potentially disrupting traditional
healthcare models.
-
Emerging Markets: Apple's growth in India and
Southeast Asia is a key opportunity as millions of consumers enter
the middle class and seek premium tech.
-
Subscription Ecosystem: Apple’s expanding lineup of
subscription services—like Music, iCloud+, and Fitness+—build
recurring revenue and customer lock-in, boosting long-term financial
stability.
8. Conclusion – Why Investors Care
Apple remains one of the most valuable and influential companies in
the world—not just because of its products, but because of its brand
strength, financial discipline, and constant innovation. Its tight
ecosystem, loyal customer base, and growing service revenues give it
long-term resilience, even in competitive or uncertain markets.
While Apple faces challenges such as regulatory pressure and market
saturation, its strategic focus on privacy, sustainability, and
emerging technologies like AI and AR/VR positions it well for future
growth. For investors, Apple offers a rare blend of profitability,
stability, and innovation that continues to shape the global tech
landscape.





